Estimated Functional Capacity Relative to Age and Sex:

Conclusions:
Stress test:
- *** exercise tolerance for age and gender
- Chest pain did not*** occur during the test
- There is no electrocardiographic*** or echocardiographic evidence of ischemia
- *** Occasional PVCs noticed during exercise
- *** Low risk study
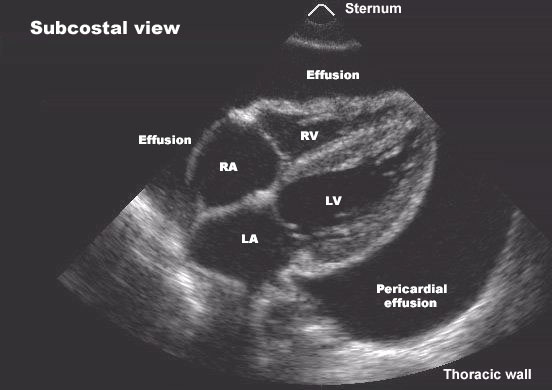
Baseline echocardiogram:
- Normal biventricular size and systolic function
- Screening 2D and Doppler is negative for significant valvular abnormalities
Pre-test Probability of CAD:

Risk Stratification:

Predicted Exercise Capacity for Age:

New Equation for Age-Predicted Maximum Heart Rate:
- Men: Max HR = 208 – (0.7 x Age)
- Women: Max HR = 206 – (0.88 x Age)
- CAD with beta-blockers: Max HR = 164 – (0.7 x Age)
Chronotropic Index Calculator:
[(HR max – HR rest) x 100] / [(220 – Age) – HR rest]
-
- Index < 80 % defines chronotropic incompetence
- With significant doses of beta-blockers, index < 62 % is considered chronotropic incompetence
Abnormal Heart Rate Recovery:
- With post-exercise cool down: Heart rate decrease by less than 12 beats/min after one minute
- With immediate exercise cessation: Heart rate decrease by less than 18 beats/min after one minute and less than 42 beats/min after 2 minutes
Blood Pressure Response:
- Exaggerated systolic pressure response: > 210 mmHg in men and > 190 mmHg in women
- Exercise-induced hypotension: Reduction of blood pressure below initial resting systolic pressure (or > 20 mmHg drop)
- Pseudo-exercise-induced hypotension: When the resting blood pressure is high and comes down with exercise
- Low systolic pressure peak: when peak blood pressure < 140 mmHg or < 10 mmHg rise in blood pressure with exercise
- Double-product reserve: Difference between resting and peak double-product is less than 10, 000